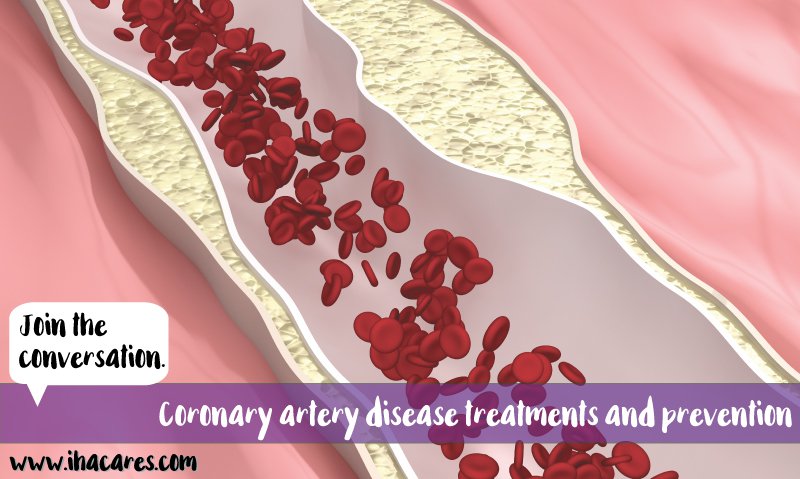
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a condition where plaque filled with cholesterol deposits in the blood vessels of the heart. As a result, your heart does not get enough blood flow and oxygen, which leads to a variety of conditions ranging from angina to heart attacks. The biggest risk factors for developing CAD are smoking, diabetes and family history. Hypertension, high cholesterol levels and poor lifestyle habits, like lack of exercise and an unhealthy diet, are also risk factors.
The best treatment of CAD is prevention. Quit smoking, control your diabetes, blood pressure and cholesterol levels. You want your LDL (bad cholesterol) to be low, and you want your HDL (good cholesterol) to be high. This can be achieved with diet, exercise and medications.
Symptoms of CAD can be vague. Chest pain is the most common symptom, but it can also present as jaw pain, neck pain, arm pain, back pain, shortness of breath or fatigue. Early recognition is key. Contrary to popular belief, women over 55-years-old carry a higher risk than men of the same age. The risk in younger men is higher than in older men.
There are various ways to treat CAD. Medications, lifestyle changes like quitting smoking, controlling your diabetes, blood pressure and cholesterol levels, as well as stents or bypass surgery. A stent is a device that looks like the spring of a ballpoint pen, which keeps arteries open. These are life-saving in situations of a heart attack. Nowadays, open heart bypass surgeries are reserved for extensive blockages in multiple areas of the heart, and/or when the blockage is in a critical part of the heart, which is not suitable for a stent.
The latest in stent technology is bioabsorbable stents, which disappear after their job of keeping the arteries open is done. These are currently being used by myself and other Michigan Heart physicians. If you have questions about CAD, please talk to your primary care physician or cardiologist.
